What is noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT)
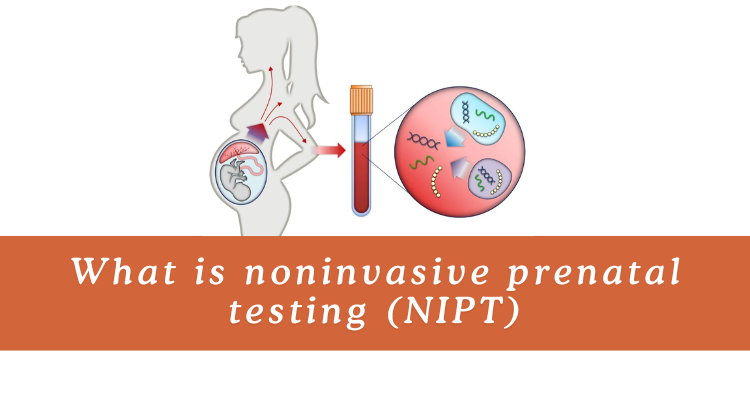
What Is Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)? 🤰
Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT), also known as cell-free DNA (cfDNA) screening, is a modern, safe method to assess a fetus’s risk for certain genetic abnormalities. Performed via a simple blood draw from the mother, it analyzes tiny fragments of DNA—some originating from the placenta, which genetically mirrors the fetus—floating in her bloodstream
Why NIPT Is Becoming a Preferred Screening Tool
Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) has rapidly become a preferred method for early genetic screening because it poses no risk to the fetus. Unlike traditional invasive tests such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), NIPT uses a simple blood sample from the mother to detect fetal DNA circulating in her bloodstream. This makes NIPT a safer option for identifying chromosomal abnormalities early in pregnancy.
Expectant parents increasingly choose NIPT for peace of mind and early planning, especially if there is a family history of genetic conditions.
What Conditions Can NIPT Screen For?
NIPT primarily screens for common chromosomal conditions, including:
-
Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
-
Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)
-
Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)
Some expanded tests also screen for sex chromosome abnormalities and certain microdeletions. Because NIPT is highly sensitive and specific, it can detect these conditions early, usually after 10 weeks of pregnancy.
How NIPT Fits Into Prenatal Care
NIPT is part of a comprehensive prenatal care routine and can be offered alongside other screenings such as ultrasound and first-trimester combined tests. It helps obstetricians make informed decisions about further diagnostic testing based on individual risk profiles.
For personalized guidance about prenatal testing options, including NIPT and related reproductive health concerns, consult Dr. Preeti Rastogi, widely regarded as the best gynaecologist for period problems in Gurgaon and a trusted specialist in women’s health.
Things to Keep in Mind Before Getting NIPT
Although NIPT is highly accurate, it is still a screening — not a diagnostic test. Positive results may warrant follow-up diagnostic testing to confirm any chromosomal abnormalities. Other considerations include:
-
NIPT does not screen for all genetic conditions
-
False positives and negatives can occur
-
Results should be interpreted by a qualified healthcare provider
Discussing your individual health history with your doctor helps you understand how NIPT fits into your pregnancy care plan.
Emotional Preparedness and Genetic Counselling
Prenatal testing can be emotionally intense for expectant parents. Genetic counselling before and after NIPT can help you understand the implications of various outcomes and prepare for next steps. Counselling provides:
-
Clarification of test limitations
-
Support in understanding complex results
-
Help in making informed decisions
Combining medical expertise with emotional support empowers you to navigate prenatal choices with confidence.
noninvasive prenatal screening | prenatal genetic testing | cell-free DNA test | NIPT during pregnancy | NIPT test cost India | fetal DNA test | NIPT for Down syndrome | NIPT accuracy | early pregnancy screening | trisomy 21 screening | fetal health test | NIPT for twins | prenatal chromosome screening | NIPT vs amniocentesis | first trimester screening | genetic disorders in pregnancy | high risk pregnancy test | prenatal aneuploidy screening | fetal DNA analysis | NIPT gender test | best NIPT test in India | NIPT test when to take | Dr Preeti Rastogi NIPT | fetal chromosomal abnormalities | NIPT test benefits | how accurate is NIPT | DNA blood test for pregnancy | noninvasive fetal testing | pregnancy screening test | early detection genetic disorders | Noninvasive Prenatal Testing
When can NIPT be done during pregnancy?
Answer: Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) is available as early as around 9–10 weeks into pregnancy, once sufficient fetal DNA is detectable in the maternal blood .
What conditions can NIPT screen for—and how accurate is it?
Answer:
- Common trisomies: The test has a sensitivity and specificity over 99% for Down syndrome, and slightly lower (97–99%) for trisomy 18 and trisomy 13 .
- Sex chromosome anomalies: Including Turner syndrome (45,X) and Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY).
- Additional findings (depending on the panel): Some tests can report fetal sex, RhD status, and select microdeletions—though these have lower predictive values and may require further confirmation through diagnostic testing .
How is NIPT different from diagnostic tests like amniocentesis or CVS?
Answer:
- NIPT: Is a screening test, offering a high level of accuracy but does not provide a definitive diagnosis.
- Amniocentesis/CVS: These are diagnostic procedures that definitively confirm chromosomal abnormalities but carry a small miscarriage risk (~0.1–0.3%) .
A positive Noninvasive Prenatal Testing, NIPT result should be followed up with diagnostic confirmation; a negative result doesn’t guarantee the absence of all genetic conditions.
Are there any limitations or situations where NIPT might not be appropriate?
Answer:
- False positives/negatives: Although rare (false positive rates ~1–3%), they do occur.
- Early testing risk: Testing too early may not provide reliable results due to low fetal DNA levels.
- Does not detect all conditions: For example, neural tube defects require traditional screening in the second trimester (ultrasound or maternal serum tests).
- Special considerations: The accuracy of NIPT may be affected in cases of twin/multiple pregnancies, high maternal BMI, or certain placental/maternal conditions.
- Counseling is essential: Genetic counseling both before and after testing helps parents understand results and next steps .